Understanding Digital Logic Design
Extra materials for the combined MIPSfpga and Connected MCU seminar by Imagination Technologies
October-November 2016
Quiz 2.4. Synthesis
Name ___________________________________________________________________
Write near each schematic diagram the name of the corresponding module:
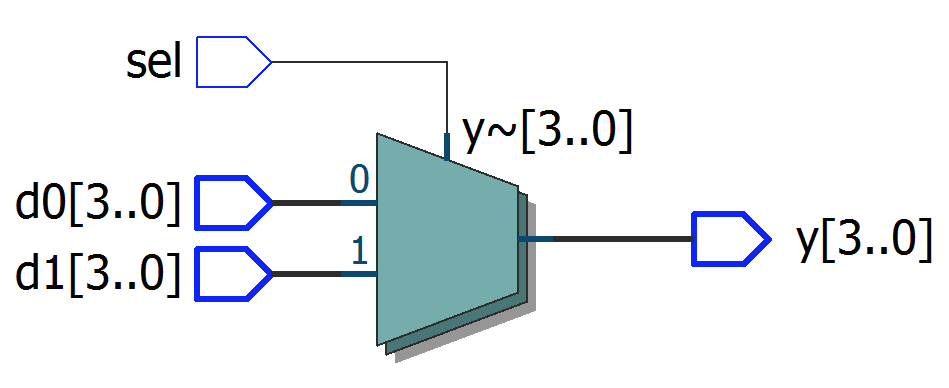
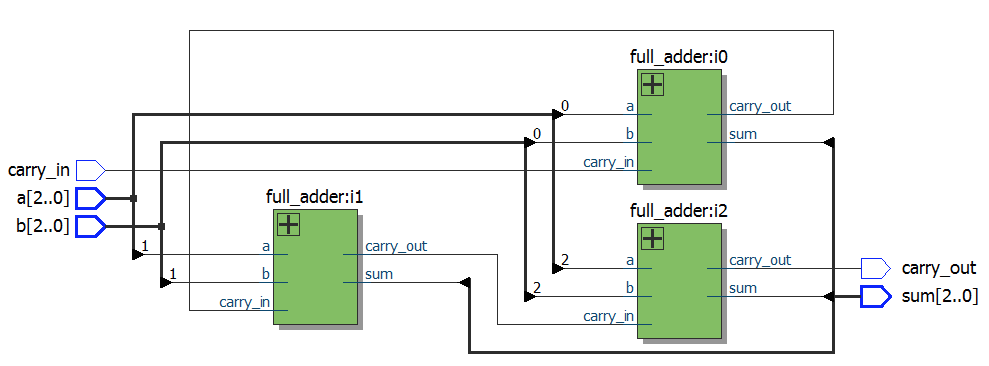
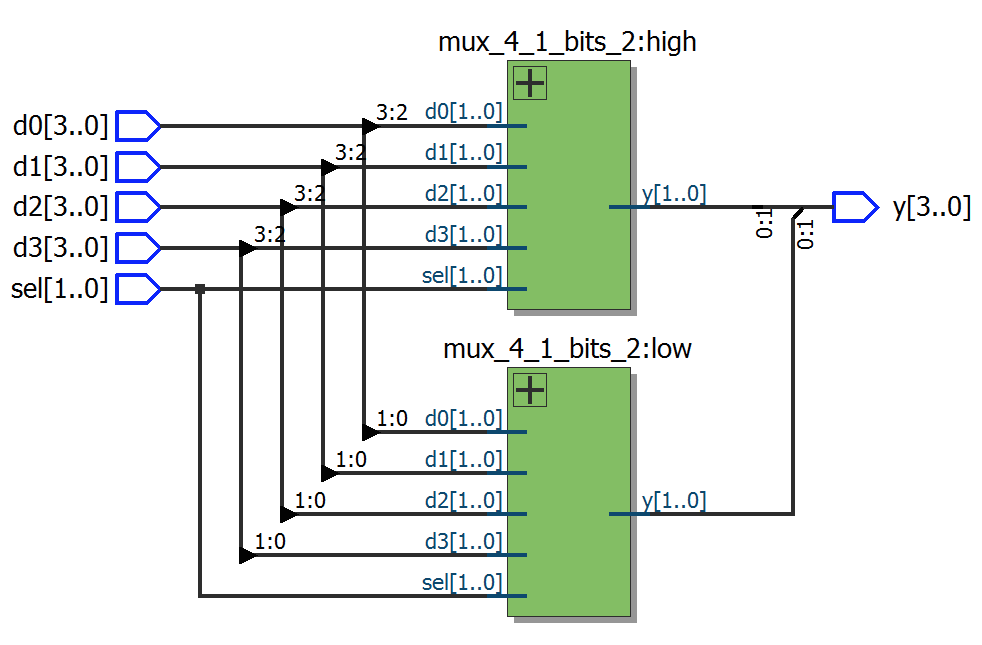
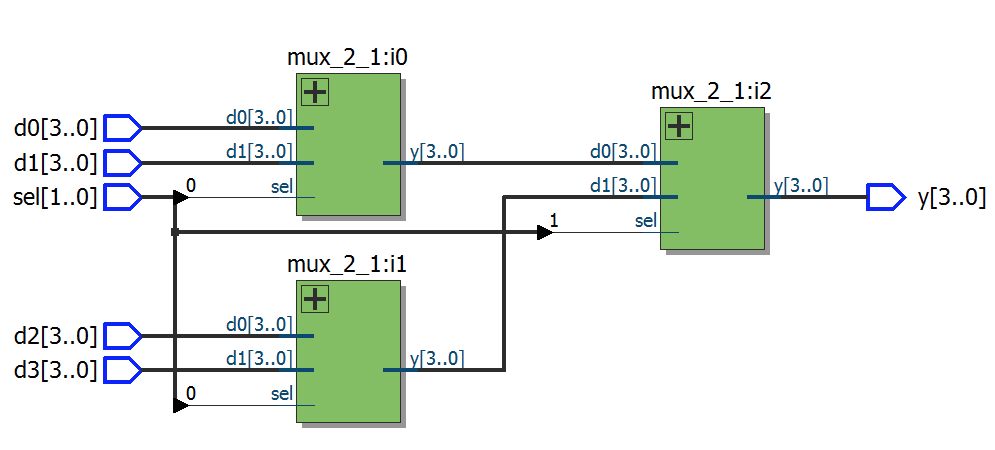
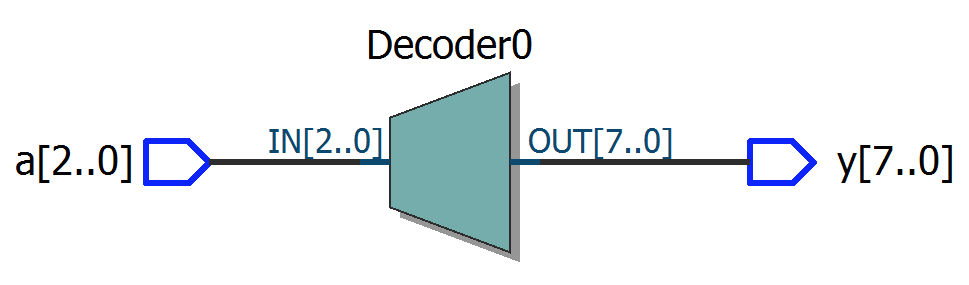
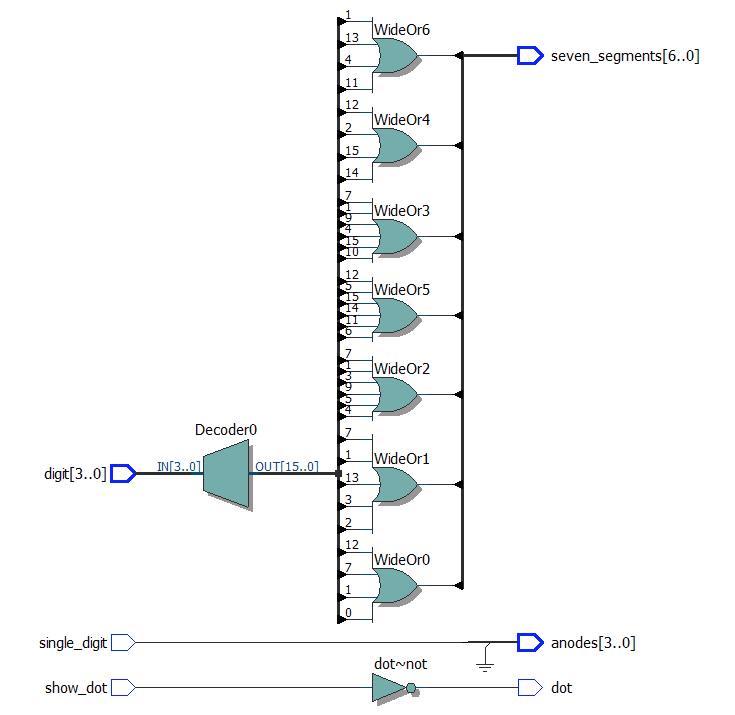
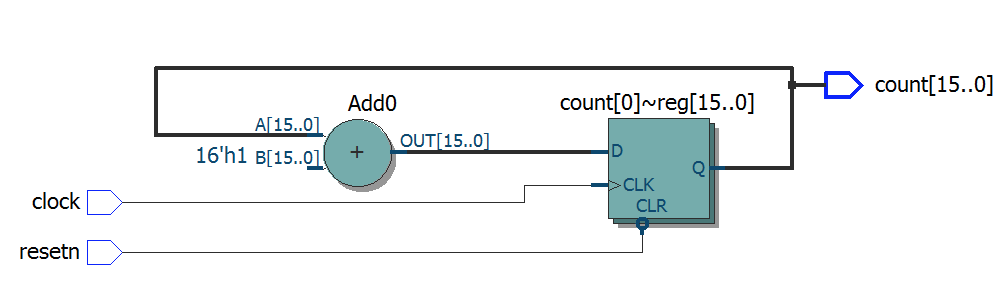
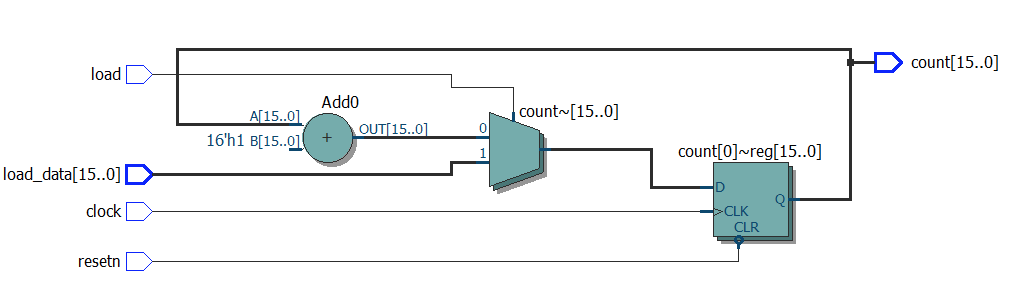
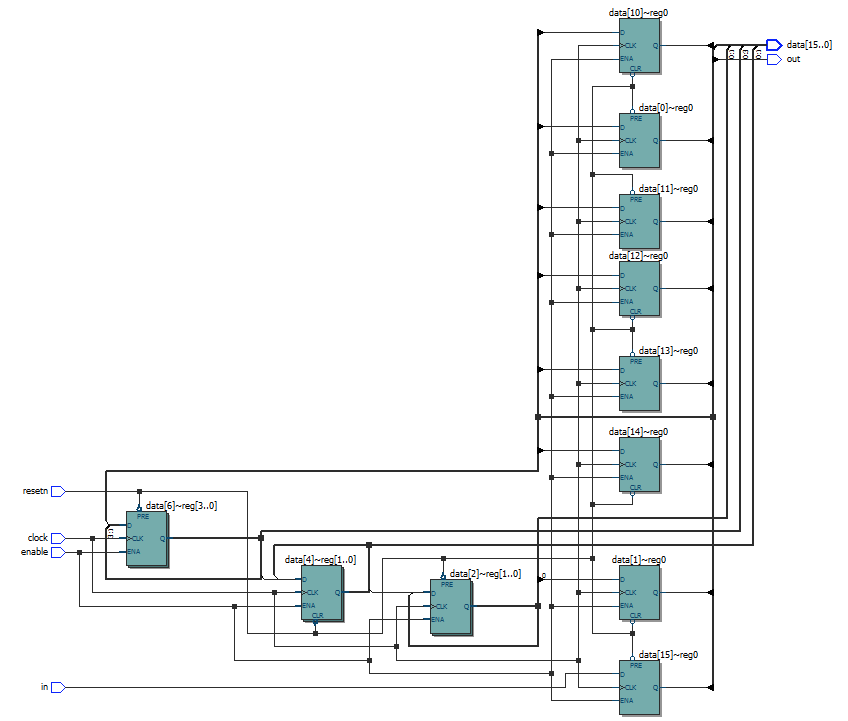
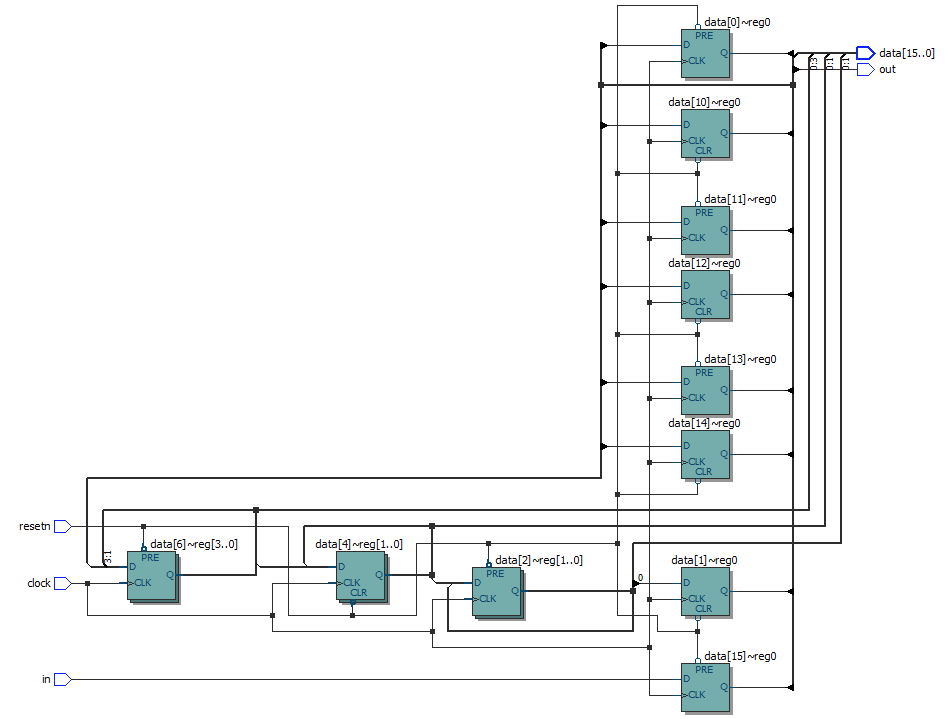
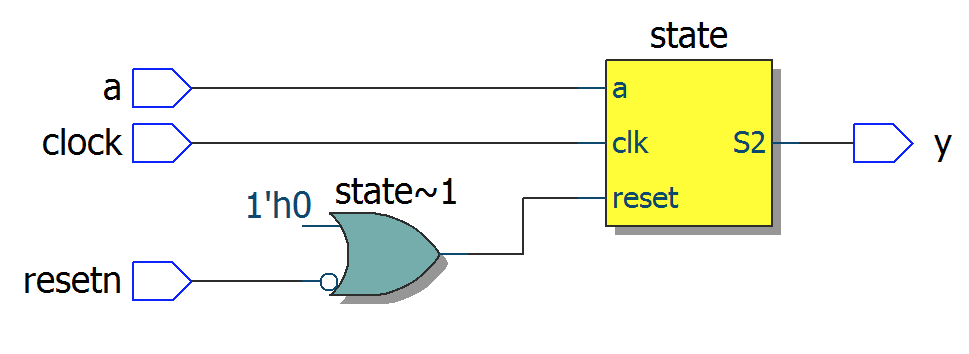
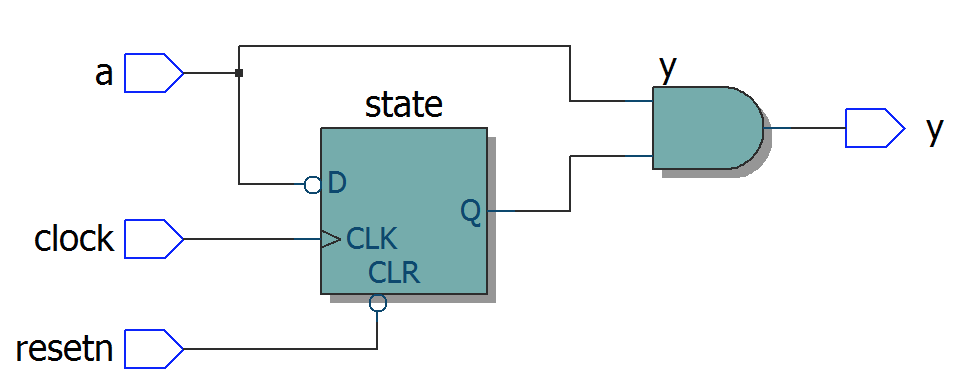 module top1
(
input a,
input b,
input carry_in,
output reg sum,
output reg carry_out
);
reg p, q;
always @*
begin
p = a ^ b;
q = a & b;
sum = p ^ carry_in;
carry_out = q | (p & carry_in);
end
endmodule
module top2
(
input clock,
input resetn,
input a,
output y
);
parameter S0 = 0, S1 = 1;
reg state, next_state;
// state register
always @ (posedge clock or negedge resetn)
if (! resetn)
state <= S0;
else
state <= next_state;
// next state logic
always @*
case (state)
S0:
if (a)
next_state = S0;
else
next_state = S1;
S1:
if (a)
next_state = S0;
else
next_state = S1;
default:
next_state = S0;
endcase
// output logic
assign y = (a & state == S1);
endmodule
module top3
(
input [3:0] digit,
input single_digit,
input show_dot,
output reg [6:0] seven_segments,
output dot,
output [3:0] anodes
);
always @*
case (digit)
'h0: seven_segments = 'b1000000; // a b c d e f g
'h1: seven_segments = 'b1111001;
'h2: seven_segments = 'b0100100; // --a--
'h3: seven_segments = 'b0110000; // | |
'h4: seven_segments = 'b0011001; // f b
'h5: seven_segments = 'b0010010; // | |
'h6: seven_segments = 'b0000010; // --g--
'h7: seven_segments = 'b1111000; // | |
'h8: seven_segments = 'b0000000; // e c
'h9: seven_segments = 'b0011000; // | |
'ha: seven_segments = 'b0001000; // --d--
'hb: seven_segments = 'b0000011;
'hc: seven_segments = 'b1000110;
'hd: seven_segments = 'b0100001;
'he: seven_segments = 'b0000110;
'hf: seven_segments = 'b0001110;
endcase
assign dot = ~ show_dot;
assign anodes = single_digit ? 4'b1110 : 4'b0000;
endmodule
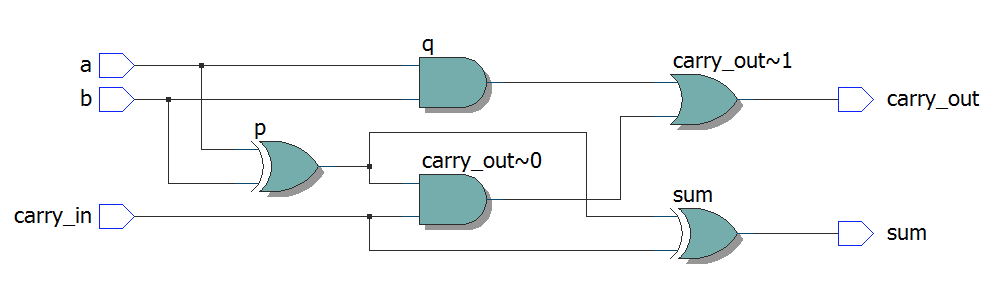
module top4
(
input [2:0] a,
input [2:0] b,
input carry_in,
output [2:0] sum,
output carry_out
);
wire c0, c1;
full_adder i0
(
.a ( a [0] ),
.b ( b [0] ),
.carry_in ( carry_in ),
.sum ( sum [0] ),
.carry_out ( c0 )
);
full_adder i1
(
.a ( a [1] ),
.b ( b [1] ),
.carry_in ( c0 ),
.sum ( sum [1] ),
.carry_out ( c1 )
);
full_adder i2
(
.a ( a [2] ),
.b ( b [2] ),
.carry_in ( c1 ),
.sum ( sum [2] ),
.carry_out ( carry_out )
);
endmodule
module top5
(
input clock,
input resetn,
output reg [15:0] count
);
always @ (posedge clock or negedge resetn)
begin
if (! resetn)
count <= 0;
else
count <= count + 1;
end
endmodule
module top6
(
input clock,
input resetn,
input in,
output out,
output reg [15:0] data
);
always @ (posedge clock or negedge resetn)
begin
if (! resetn)
data <= 16'hABCD;
else
data <= { in, data [15:1] };
// data <= (data >> 1) | (in << 15);
end
assign out = data [0];
endmodule
module top7
(
input clock,
input resetn,
input in,
input enable,
output out,
output reg [15:0] data
);
always @ (posedge clock or negedge resetn)
begin
if (! resetn)
data <= 16'hABCD;
else if (enable)
data <= { in, data [15:1] };
// data <= (data >> 1) | (in << 15);
end
assign out = data [0];
endmodule
module top8
(
input clock,
input resetn,
input a,
output y
);
parameter [1:0] S0 = 0, S1 = 1, S2 = 2;
reg [1:0] state, next_state;
// state register
always @ (posedge clock or negedge resetn)
if (! resetn)
state <= S0;
else
state <= next_state;
// next state logic
always @*
case (state)
S0:
if (a)
next_state = S0;
else
next_state = S1;
S1:
if (a)
next_state = S2;
else
next_state = S1;
S2:
if (a)
next_state = S0;
else
next_state = S1;
default:
next_state = S0;
endcase
// output logic
assign y = (state == S2);
endmodule
module top9
(
input clock,
input resetn,
input load,
input [15:0] load_data,
output reg [15:0] count
);
always @ (posedge clock or negedge resetn)
begin
if (! resetn)
count <= 0;
else if (load)
count <= load_data;
else
count <= count + 1;
end
endmodule
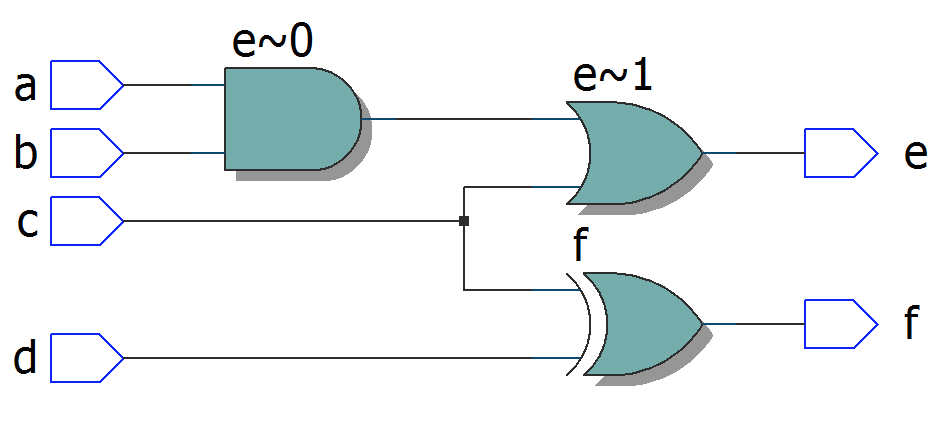
module top10
(
input a, b, c, d,
output e, f
);
assign e = a & (b | c);
assign f = c ^ d;
endmodule
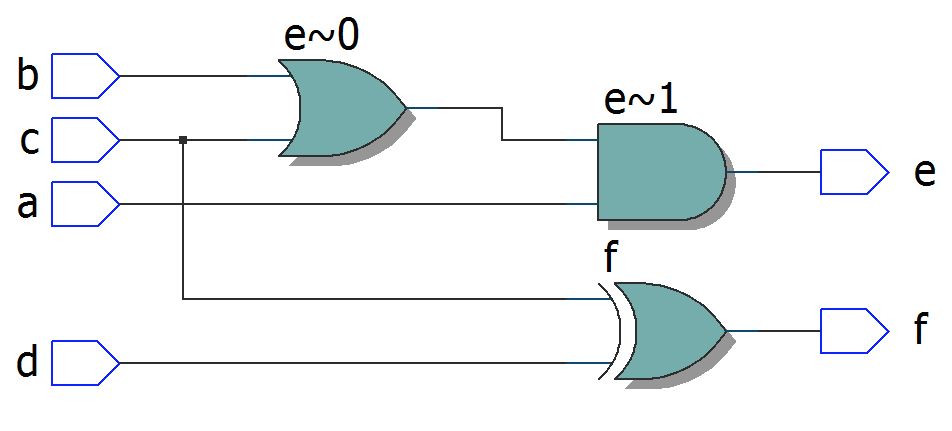
module top11
(
input a, b, c, d,
output e, f
);
assign e = a & b | c;
assign f = c ^ d;
endmodule
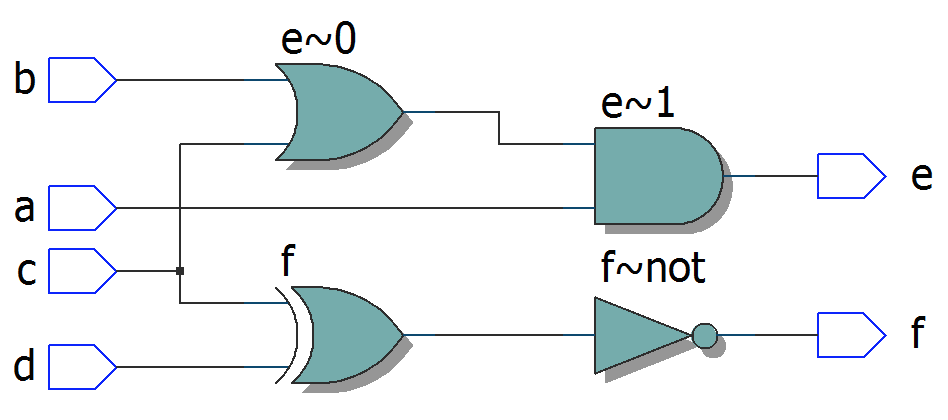
module top12
(
input a, b, c, d,
output e, f
);
assign e = a & (b | c);
assign f = ~ (c ^ d);
endmodule
module top13
(
input [3:0] d0,
input [3:0] d1,
input sel,
output [3:0] y
);
assign y = sel ? d1 : d0;
endmodule
module top14
(
input [3:0] d0, d1, d2, d3,
input [1:0] sel,
output [3:0] y
);
wire [3:0] w01, w23;
mux_2_1 i0 (.d0 ( d0 ), .d1 ( d1 ), .sel (sel [0]), .y ( w01 ));
mux_2_1 i1 (.d0 ( d2 ), .d1 ( d3 ), .sel (sel [0]), .y ( w23 ));
mux_2_1 i2 (.d0 ( w01 ), .d1 ( w23 ), .sel (sel [1]), .y ( y ));
endmodule
module top15
(
input [3:0] d0, d1, d2, d3,
input [1:0] sel,
output [3:0] y
);
mux_4_1_bits_2 high
(
.d0 ( d0 [3:2] ),
.d1 ( d1 [3:2] ),
.d2 ( d2 [3:2] ),
.d3 ( d3 [3:2] ),
.sel ( sel ),
.y ( y [3:2] )
);
mux_4_1_bits_2 low
(
.d0 ( d0 [1:0] ),
.d1 ( d1 [1:0] ),
.d2 ( d2 [1:0] ),
.d3 ( d3 [1:0] ),
.sel ( sel ),
.y ( y [1:0] )
);
endmodule
module top16
(
input [2:0] a,
output reg [7:0] y
);
always @*
case (a)
3'b000: y = 8'b00000001;
3'b001: y = 8'b00000010;
3'b010: y = 8'b00000100;
3'b011: y = 8'b00001000;
3'b100: y = 8'b00010000;
3'b101: y = 8'b00100000;
3'b110: y = 8'b01000000;
3'b111: y = 8'b10000000;
endcase
endmodule
Quiz is created by Yuri Panchul
module top1
(
input a,
input b,
input carry_in,
output reg sum,
output reg carry_out
);
reg p, q;
always @*
begin
p = a ^ b;
q = a & b;
sum = p ^ carry_in;
carry_out = q | (p & carry_in);
end
endmodule
module top2
(
input clock,
input resetn,
input a,
output y
);
parameter S0 = 0, S1 = 1;
reg state, next_state;
// state register
always @ (posedge clock or negedge resetn)
if (! resetn)
state <= S0;
else
state <= next_state;
// next state logic
always @*
case (state)
S0:
if (a)
next_state = S0;
else
next_state = S1;
S1:
if (a)
next_state = S0;
else
next_state = S1;
default:
next_state = S0;
endcase
// output logic
assign y = (a & state == S1);
endmodule
module top3
(
input [3:0] digit,
input single_digit,
input show_dot,
output reg [6:0] seven_segments,
output dot,
output [3:0] anodes
);
always @*
case (digit)
'h0: seven_segments = 'b1000000; // a b c d e f g
'h1: seven_segments = 'b1111001;
'h2: seven_segments = 'b0100100; // --a--
'h3: seven_segments = 'b0110000; // | |
'h4: seven_segments = 'b0011001; // f b
'h5: seven_segments = 'b0010010; // | |
'h6: seven_segments = 'b0000010; // --g--
'h7: seven_segments = 'b1111000; // | |
'h8: seven_segments = 'b0000000; // e c
'h9: seven_segments = 'b0011000; // | |
'ha: seven_segments = 'b0001000; // --d--
'hb: seven_segments = 'b0000011;
'hc: seven_segments = 'b1000110;
'hd: seven_segments = 'b0100001;
'he: seven_segments = 'b0000110;
'hf: seven_segments = 'b0001110;
endcase
assign dot = ~ show_dot;
assign anodes = single_digit ? 4'b1110 : 4'b0000;
endmodule
module top4
(
input [2:0] a,
input [2:0] b,
input carry_in,
output [2:0] sum,
output carry_out
);
wire c0, c1;
full_adder i0
(
.a ( a [0] ),
.b ( b [0] ),
.carry_in ( carry_in ),
.sum ( sum [0] ),
.carry_out ( c0 )
);
full_adder i1
(
.a ( a [1] ),
.b ( b [1] ),
.carry_in ( c0 ),
.sum ( sum [1] ),
.carry_out ( c1 )
);
full_adder i2
(
.a ( a [2] ),
.b ( b [2] ),
.carry_in ( c1 ),
.sum ( sum [2] ),
.carry_out ( carry_out )
);
endmodule
module top5
(
input clock,
input resetn,
output reg [15:0] count
);
always @ (posedge clock or negedge resetn)
begin
if (! resetn)
count <= 0;
else
count <= count + 1;
end
endmodule
module top6
(
input clock,
input resetn,
input in,
output out,
output reg [15:0] data
);
always @ (posedge clock or negedge resetn)
begin
if (! resetn)
data <= 16'hABCD;
else
data <= { in, data [15:1] };
// data <= (data >> 1) | (in << 15);
end
assign out = data [0];
endmodule
module top7
(
input clock,
input resetn,
input in,
input enable,
output out,
output reg [15:0] data
);
always @ (posedge clock or negedge resetn)
begin
if (! resetn)
data <= 16'hABCD;
else if (enable)
data <= { in, data [15:1] };
// data <= (data >> 1) | (in << 15);
end
assign out = data [0];
endmodule
module top8
(
input clock,
input resetn,
input a,
output y
);
parameter [1:0] S0 = 0, S1 = 1, S2 = 2;
reg [1:0] state, next_state;
// state register
always @ (posedge clock or negedge resetn)
if (! resetn)
state <= S0;
else
state <= next_state;
// next state logic
always @*
case (state)
S0:
if (a)
next_state = S0;
else
next_state = S1;
S1:
if (a)
next_state = S2;
else
next_state = S1;
S2:
if (a)
next_state = S0;
else
next_state = S1;
default:
next_state = S0;
endcase
// output logic
assign y = (state == S2);
endmodule
module top9
(
input clock,
input resetn,
input load,
input [15:0] load_data,
output reg [15:0] count
);
always @ (posedge clock or negedge resetn)
begin
if (! resetn)
count <= 0;
else if (load)
count <= load_data;
else
count <= count + 1;
end
endmodule
module top10
(
input a, b, c, d,
output e, f
);
assign e = a & (b | c);
assign f = c ^ d;
endmodule
module top11
(
input a, b, c, d,
output e, f
);
assign e = a & b | c;
assign f = c ^ d;
endmodule
module top12
(
input a, b, c, d,
output e, f
);
assign e = a & (b | c);
assign f = ~ (c ^ d);
endmodule
module top13
(
input [3:0] d0,
input [3:0] d1,
input sel,
output [3:0] y
);
assign y = sel ? d1 : d0;
endmodule
module top14
(
input [3:0] d0, d1, d2, d3,
input [1:0] sel,
output [3:0] y
);
wire [3:0] w01, w23;
mux_2_1 i0 (.d0 ( d0 ), .d1 ( d1 ), .sel (sel [0]), .y ( w01 ));
mux_2_1 i1 (.d0 ( d2 ), .d1 ( d3 ), .sel (sel [0]), .y ( w23 ));
mux_2_1 i2 (.d0 ( w01 ), .d1 ( w23 ), .sel (sel [1]), .y ( y ));
endmodule
module top15
(
input [3:0] d0, d1, d2, d3,
input [1:0] sel,
output [3:0] y
);
mux_4_1_bits_2 high
(
.d0 ( d0 [3:2] ),
.d1 ( d1 [3:2] ),
.d2 ( d2 [3:2] ),
.d3 ( d3 [3:2] ),
.sel ( sel ),
.y ( y [3:2] )
);
mux_4_1_bits_2 low
(
.d0 ( d0 [1:0] ),
.d1 ( d1 [1:0] ),
.d2 ( d2 [1:0] ),
.d3 ( d3 [1:0] ),
.sel ( sel ),
.y ( y [1:0] )
);
endmodule
module top16
(
input [2:0] a,
output reg [7:0] y
);
always @*
case (a)
3'b000: y = 8'b00000001;
3'b001: y = 8'b00000010;
3'b010: y = 8'b00000100;
3'b011: y = 8'b00001000;
3'b100: y = 8'b00010000;
3'b101: y = 8'b00100000;
3'b110: y = 8'b01000000;
3'b111: y = 8'b10000000;
endcase
endmodule
Quiz is created by Yuri Panchul















 module top1
(
input a,
input b,
input carry_in,
output reg sum,
output reg carry_out
);
reg p, q;
always @*
begin
p = a ^ b;
q = a & b;
sum = p ^ carry_in;
carry_out = q | (p & carry_in);
end
endmodule
module top2
(
input clock,
input resetn,
input a,
output y
);
parameter S0 = 0, S1 = 1;
reg state, next_state;
// state register
always @ (posedge clock or negedge resetn)
if (! resetn)
state <= S0;
else
state <= next_state;
// next state logic
always @*
case (state)
S0:
if (a)
next_state = S0;
else
next_state = S1;
S1:
if (a)
next_state = S0;
else
next_state = S1;
default:
next_state = S0;
endcase
// output logic
assign y = (a & state == S1);
endmodule
module top3
(
input [3:0] digit,
input single_digit,
input show_dot,
output reg [6:0] seven_segments,
output dot,
output [3:0] anodes
);
always @*
case (digit)
'h0: seven_segments = 'b1000000; // a b c d e f g
'h1: seven_segments = 'b1111001;
'h2: seven_segments = 'b0100100; // --a--
'h3: seven_segments = 'b0110000; // | |
'h4: seven_segments = 'b0011001; // f b
'h5: seven_segments = 'b0010010; // | |
'h6: seven_segments = 'b0000010; // --g--
'h7: seven_segments = 'b1111000; // | |
'h8: seven_segments = 'b0000000; // e c
'h9: seven_segments = 'b0011000; // | |
'ha: seven_segments = 'b0001000; // --d--
'hb: seven_segments = 'b0000011;
'hc: seven_segments = 'b1000110;
'hd: seven_segments = 'b0100001;
'he: seven_segments = 'b0000110;
'hf: seven_segments = 'b0001110;
endcase
assign dot = ~ show_dot;
assign anodes = single_digit ? 4'b1110 : 4'b0000;
endmodule
module top4
(
input [2:0] a,
input [2:0] b,
input carry_in,
output [2:0] sum,
output carry_out
);
wire c0, c1;
full_adder i0
(
.a ( a [0] ),
.b ( b [0] ),
.carry_in ( carry_in ),
.sum ( sum [0] ),
.carry_out ( c0 )
);
full_adder i1
(
.a ( a [1] ),
.b ( b [1] ),
.carry_in ( c0 ),
.sum ( sum [1] ),
.carry_out ( c1 )
);
full_adder i2
(
.a ( a [2] ),
.b ( b [2] ),
.carry_in ( c1 ),
.sum ( sum [2] ),
.carry_out ( carry_out )
);
endmodule
module top5
(
input clock,
input resetn,
output reg [15:0] count
);
always @ (posedge clock or negedge resetn)
begin
if (! resetn)
count <= 0;
else
count <= count + 1;
end
endmodule
module top6
(
input clock,
input resetn,
input in,
output out,
output reg [15:0] data
);
always @ (posedge clock or negedge resetn)
begin
if (! resetn)
data <= 16'hABCD;
else
data <= { in, data [15:1] };
// data <= (data >> 1) | (in << 15);
end
assign out = data [0];
endmodule
module top7
(
input clock,
input resetn,
input in,
input enable,
output out,
output reg [15:0] data
);
always @ (posedge clock or negedge resetn)
begin
if (! resetn)
data <= 16'hABCD;
else if (enable)
data <= { in, data [15:1] };
// data <= (data >> 1) | (in << 15);
end
assign out = data [0];
endmodule
module top8
(
input clock,
input resetn,
input a,
output y
);
parameter [1:0] S0 = 0, S1 = 1, S2 = 2;
reg [1:0] state, next_state;
// state register
always @ (posedge clock or negedge resetn)
if (! resetn)
state <= S0;
else
state <= next_state;
// next state logic
always @*
case (state)
S0:
if (a)
next_state = S0;
else
next_state = S1;
S1:
if (a)
next_state = S2;
else
next_state = S1;
S2:
if (a)
next_state = S0;
else
next_state = S1;
default:
next_state = S0;
endcase
// output logic
assign y = (state == S2);
endmodule
module top9
(
input clock,
input resetn,
input load,
input [15:0] load_data,
output reg [15:0] count
);
always @ (posedge clock or negedge resetn)
begin
if (! resetn)
count <= 0;
else if (load)
count <= load_data;
else
count <= count + 1;
end
endmodule
module top10
(
input a, b, c, d,
output e, f
);
assign e = a & (b | c);
assign f = c ^ d;
endmodule
module top11
(
input a, b, c, d,
output e, f
);
assign e = a & b | c;
assign f = c ^ d;
endmodule
module top12
(
input a, b, c, d,
output e, f
);
assign e = a & (b | c);
assign f = ~ (c ^ d);
endmodule
module top13
(
input [3:0] d0,
input [3:0] d1,
input sel,
output [3:0] y
);
assign y = sel ? d1 : d0;
endmodule
module top14
(
input [3:0] d0, d1, d2, d3,
input [1:0] sel,
output [3:0] y
);
wire [3:0] w01, w23;
mux_2_1 i0 (.d0 ( d0 ), .d1 ( d1 ), .sel (sel [0]), .y ( w01 ));
mux_2_1 i1 (.d0 ( d2 ), .d1 ( d3 ), .sel (sel [0]), .y ( w23 ));
mux_2_1 i2 (.d0 ( w01 ), .d1 ( w23 ), .sel (sel [1]), .y ( y ));
endmodule
module top15
(
input [3:0] d0, d1, d2, d3,
input [1:0] sel,
output [3:0] y
);
mux_4_1_bits_2 high
(
.d0 ( d0 [3:2] ),
.d1 ( d1 [3:2] ),
.d2 ( d2 [3:2] ),
.d3 ( d3 [3:2] ),
.sel ( sel ),
.y ( y [3:2] )
);
mux_4_1_bits_2 low
(
.d0 ( d0 [1:0] ),
.d1 ( d1 [1:0] ),
.d2 ( d2 [1:0] ),
.d3 ( d3 [1:0] ),
.sel ( sel ),
.y ( y [1:0] )
);
endmodule
module top16
(
input [2:0] a,
output reg [7:0] y
);
always @*
case (a)
3'b000: y = 8'b00000001;
3'b001: y = 8'b00000010;
3'b010: y = 8'b00000100;
3'b011: y = 8'b00001000;
3'b100: y = 8'b00010000;
3'b101: y = 8'b00100000;
3'b110: y = 8'b01000000;
3'b111: y = 8'b10000000;
endcase
endmodule
Quiz is created by Yuri Panchul
module top1
(
input a,
input b,
input carry_in,
output reg sum,
output reg carry_out
);
reg p, q;
always @*
begin
p = a ^ b;
q = a & b;
sum = p ^ carry_in;
carry_out = q | (p & carry_in);
end
endmodule
module top2
(
input clock,
input resetn,
input a,
output y
);
parameter S0 = 0, S1 = 1;
reg state, next_state;
// state register
always @ (posedge clock or negedge resetn)
if (! resetn)
state <= S0;
else
state <= next_state;
// next state logic
always @*
case (state)
S0:
if (a)
next_state = S0;
else
next_state = S1;
S1:
if (a)
next_state = S0;
else
next_state = S1;
default:
next_state = S0;
endcase
// output logic
assign y = (a & state == S1);
endmodule
module top3
(
input [3:0] digit,
input single_digit,
input show_dot,
output reg [6:0] seven_segments,
output dot,
output [3:0] anodes
);
always @*
case (digit)
'h0: seven_segments = 'b1000000; // a b c d e f g
'h1: seven_segments = 'b1111001;
'h2: seven_segments = 'b0100100; // --a--
'h3: seven_segments = 'b0110000; // | |
'h4: seven_segments = 'b0011001; // f b
'h5: seven_segments = 'b0010010; // | |
'h6: seven_segments = 'b0000010; // --g--
'h7: seven_segments = 'b1111000; // | |
'h8: seven_segments = 'b0000000; // e c
'h9: seven_segments = 'b0011000; // | |
'ha: seven_segments = 'b0001000; // --d--
'hb: seven_segments = 'b0000011;
'hc: seven_segments = 'b1000110;
'hd: seven_segments = 'b0100001;
'he: seven_segments = 'b0000110;
'hf: seven_segments = 'b0001110;
endcase
assign dot = ~ show_dot;
assign anodes = single_digit ? 4'b1110 : 4'b0000;
endmodule
module top4
(
input [2:0] a,
input [2:0] b,
input carry_in,
output [2:0] sum,
output carry_out
);
wire c0, c1;
full_adder i0
(
.a ( a [0] ),
.b ( b [0] ),
.carry_in ( carry_in ),
.sum ( sum [0] ),
.carry_out ( c0 )
);
full_adder i1
(
.a ( a [1] ),
.b ( b [1] ),
.carry_in ( c0 ),
.sum ( sum [1] ),
.carry_out ( c1 )
);
full_adder i2
(
.a ( a [2] ),
.b ( b [2] ),
.carry_in ( c1 ),
.sum ( sum [2] ),
.carry_out ( carry_out )
);
endmodule
module top5
(
input clock,
input resetn,
output reg [15:0] count
);
always @ (posedge clock or negedge resetn)
begin
if (! resetn)
count <= 0;
else
count <= count + 1;
end
endmodule
module top6
(
input clock,
input resetn,
input in,
output out,
output reg [15:0] data
);
always @ (posedge clock or negedge resetn)
begin
if (! resetn)
data <= 16'hABCD;
else
data <= { in, data [15:1] };
// data <= (data >> 1) | (in << 15);
end
assign out = data [0];
endmodule
module top7
(
input clock,
input resetn,
input in,
input enable,
output out,
output reg [15:0] data
);
always @ (posedge clock or negedge resetn)
begin
if (! resetn)
data <= 16'hABCD;
else if (enable)
data <= { in, data [15:1] };
// data <= (data >> 1) | (in << 15);
end
assign out = data [0];
endmodule
module top8
(
input clock,
input resetn,
input a,
output y
);
parameter [1:0] S0 = 0, S1 = 1, S2 = 2;
reg [1:0] state, next_state;
// state register
always @ (posedge clock or negedge resetn)
if (! resetn)
state <= S0;
else
state <= next_state;
// next state logic
always @*
case (state)
S0:
if (a)
next_state = S0;
else
next_state = S1;
S1:
if (a)
next_state = S2;
else
next_state = S1;
S2:
if (a)
next_state = S0;
else
next_state = S1;
default:
next_state = S0;
endcase
// output logic
assign y = (state == S2);
endmodule
module top9
(
input clock,
input resetn,
input load,
input [15:0] load_data,
output reg [15:0] count
);
always @ (posedge clock or negedge resetn)
begin
if (! resetn)
count <= 0;
else if (load)
count <= load_data;
else
count <= count + 1;
end
endmodule
module top10
(
input a, b, c, d,
output e, f
);
assign e = a & (b | c);
assign f = c ^ d;
endmodule
module top11
(
input a, b, c, d,
output e, f
);
assign e = a & b | c;
assign f = c ^ d;
endmodule
module top12
(
input a, b, c, d,
output e, f
);
assign e = a & (b | c);
assign f = ~ (c ^ d);
endmodule
module top13
(
input [3:0] d0,
input [3:0] d1,
input sel,
output [3:0] y
);
assign y = sel ? d1 : d0;
endmodule
module top14
(
input [3:0] d0, d1, d2, d3,
input [1:0] sel,
output [3:0] y
);
wire [3:0] w01, w23;
mux_2_1 i0 (.d0 ( d0 ), .d1 ( d1 ), .sel (sel [0]), .y ( w01 ));
mux_2_1 i1 (.d0 ( d2 ), .d1 ( d3 ), .sel (sel [0]), .y ( w23 ));
mux_2_1 i2 (.d0 ( w01 ), .d1 ( w23 ), .sel (sel [1]), .y ( y ));
endmodule
module top15
(
input [3:0] d0, d1, d2, d3,
input [1:0] sel,
output [3:0] y
);
mux_4_1_bits_2 high
(
.d0 ( d0 [3:2] ),
.d1 ( d1 [3:2] ),
.d2 ( d2 [3:2] ),
.d3 ( d3 [3:2] ),
.sel ( sel ),
.y ( y [3:2] )
);
mux_4_1_bits_2 low
(
.d0 ( d0 [1:0] ),
.d1 ( d1 [1:0] ),
.d2 ( d2 [1:0] ),
.d3 ( d3 [1:0] ),
.sel ( sel ),
.y ( y [1:0] )
);
endmodule
module top16
(
input [2:0] a,
output reg [7:0] y
);
always @*
case (a)
3'b000: y = 8'b00000001;
3'b001: y = 8'b00000010;
3'b010: y = 8'b00000100;
3'b011: y = 8'b00001000;
3'b100: y = 8'b00010000;
3'b101: y = 8'b00100000;
3'b110: y = 8'b01000000;
3'b111: y = 8'b10000000;
endcase
endmodule
Quiz is created by Yuri Panchul